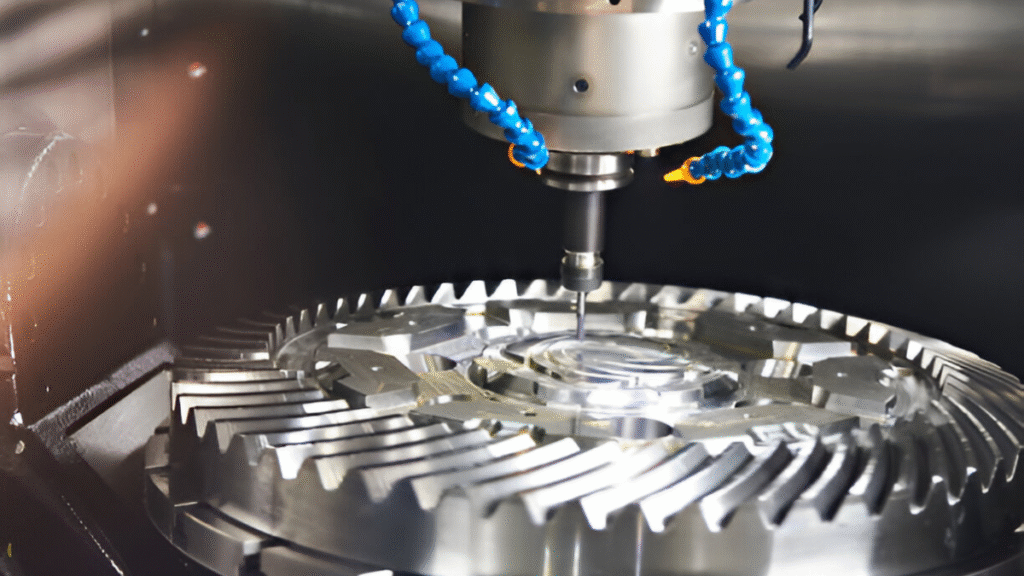
How CNC Machining Works
- CNC machining is a process used to control machine tools through computer programming. The process starts with creating a digital design of the part using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. After the design is complete, it is converted into instructions using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software. These instructions guide the CNC machine in performing the cutting, drilling, milling, or other operations to produce the part.
The CNC Process Step-by-Step
- Design: The part is designed using CAD software.
- Programming: The design is converted into instructions through CAM software.
- Machining: The CNC machine executes the instructions, shaping the material according to the design.
- Finishing: After the machining is complete, any additional finishing operations like polishing or coating may be performed.
This process ensures that parts are produced with incredible precision and consistency, making CNC machining indispensable in many fields.
Types of CNC Machines
CNC machines come in various forms, each designed for specific applications. Here are some of the most common types:
CNC Milling Machines
CNC milling machines are used to remove material from a workpiece using rotating cutters. These machines are incredibly versatile, allowing for complex shapes to be created in a variety of materials.
CNC Lathes
CNC lathes rotate the material while a cutting tool shapes it. They are primarily used for parts that require a cylindrical shape, such as shafts or pulleys.
CNC Routers
CNC routers are often used to cut large, flat materials such as wood, plastics, and metals. They can also handle more intricate tasks like engraving and carving.
CNC Plasma Cutters
Plasma cutters use a high-temperature plasma jet to cut through metals. These machines are commonly used in industries like automotive and construction, where thick metals need to be cut quickly.
CNC EDM Machines (Electrical Discharge Machining)
EDM machines use electrical sparks to erode material and shape parts. They are often used for precise, intricate cuts in hard materials.
Materials Used in CNC Machining
CNC machining is incredibly versatile when it comes to the materials it can handle. The most common materials used in CNC machining include:
Metals
- Aluminum: Lightweight, durable, and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications.
- Steel: Strong and versatile, often used in industries where strength and durability are crucial.
- Titanium: Known for its strength and lightweight, titanium is commonly used in the aerospace and medical industries.
Plastics
- ABS: Known for its toughness and impact resistance, ABS is used in a variety of consumer goods and automotive parts.
- Nylon: A strong, flexible material used in industrial applications like gears and bearings.
Composites
Composites like carbon fiber and fiberglass are becoming increasingly popular in industries like aerospace and automotive due to their high strength-to-weight ratio.
Advantages of CNC Machining
CNC machining offers numerous advantages over traditional machining methods, including:
Precision and Accuracy
CNC machines can achieve tolerances as fine as 0.0001 inches, making them ideal for high-precision industries like aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
Speed and Efficiency
Once set up, CNC machines can run continuously, producing parts at a much faster rate than manual processes. This leads to shorter lead times and lower production costs.
Cost-Effectiveness for Large Productions
While the initial setup costs of CNC machines can be high, they quickly pay for themselves with large production runs. CNC machines require less manual labor, which lowers the overall cost per part as production increases.
Consistency and Repeatability
CNC machines can produce identical parts over and over again without variation. This consistency is crucial in industries where reliability is key, such as medical device manufacturing and electronics.
Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining is used in a variety of industries, each with its own specific requirements. Some of the most common applications include:
Aerospace
CNC machining is critical in aerospace for creating lightweight, high-strength components such as turbine blades, fuselage parts, and structural components. The precision required in this field makes CNC machining the ideal choice.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, CNC machines are used to manufacture parts like engine blocks, transmissions, and suspension components. The ability to produce large volumes of precise parts is essential in this high-demand field.
Medical Devices
CNC machining is used to create custom implants, surgical tools, and diagnostic equipment. The precision of CNC machines ensures that parts fit perfectly and function as required.
Electronics
CNC machining is employed to produce small, intricate components used in consumer electronics, such as smartphones, laptops, and televisions.
CNC Machining vs Traditional Machining
When compared to traditional machining methods, CNC machining offers several advantages:
Precision and Accuracy
Traditional machining often relies on manual adjustments, which can introduce human error. CNC machining eliminates this, ensuring that parts are made to exact specifications.
Automation and Efficiency
CNC machines require less manual labor and can operate continuously. Traditional methods, on the other hand, often require frequent stops for adjustments and setup.
Complex Shapes
CNC machines can handle much more intricate designs, such as those required in the aerospace and medical industries. Traditional machining methods struggle with these complex shapes.
The Future of CNC Machining
The future of CNC machining is bright, with advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and robotics paving the way for even more efficient machines. As technology evolves, CNC machines will become faster, more precise, and more capable of handling complex tasks.
Conclusion
CNC machining is an essential technology that drives modern manufacturing. Whether you’re looking to produce a few prototypes or thousands of identical parts, CNC machining ensures precision, speed, and cost-effectiveness. As industries continue to evolve, CNC machining will remain at the heart of innovation, ensuring that the future of manufacturing is more efficient and accurate than ever before.